
Loading...

Loading...
ඔබ අසළ කිසිවෙක් නොමැති පාළු වන මංපෙතක් තුළින් ගමන් කරන අතරතුර ඔබ ඉදිරියේ පුද්ගලයෙකු බිම ඇද වැටී සිටිනු දක්නට ලැබේ. මේ අවස්ථාවේදී ඔබ කිමක් කළ යුතුද? එම පුද්ගලයාට උදවු කරන්නේ කෙසේද? මේ සියල්ලටම පිළිතුරු දීමට ඔබ වෙත Dr. ABC පැමිනෙනු ඇත. D-R-A-B-C යනු ප්රථමාධාර ලබාදීමට පෙර ඔබ කළ යුතු මූලික සමීක්ෂණය වේ. මෙහි පියවර 5 ඔබට පහසුවට Dr. ABC ලෙස මතක තබාගත හැක.
..
D for Danger (අනතුර)
..
මෙහි පළමු අදියරේදී, රෝගියා අවට පරිසරය නිරීක්ෂණය කළ යුතු වේ. රෝගියා වෙත ළඟා වීම ආරක්ෂිතද යන්න සහ ඔබ හෝ වෙනත් අයෙකු නැවත අනතුරට ලක්විය හැකි තත්ත්වයක් නොමැති බවට තහවුරු කරගත යුතුය. එම පරිසරය ඔබට අනතුරු සහගත නම්, රෝගියා වෙත ලඟා විය නොහැකිනම් අනතුර ඉවත්වන තෙක් රෝගියා වෙත ලඟාවීම නොකළ යුතුය. නැතිනම් ප්රථමාධාරකරු වන ඔබටත් අනතුරක් සිදුවිය හැක. එහෙත් එසේ අනතුරුදායක ස්වභාවයක් නැතිනම් ඔබට රෝගියා වෙත ගොස් ප්රථමාධාර කළ හැක. උදාහරණ ලෙස, බිම වැටී සිටින පුද්ගලයෙකු අසල සර්පයෙක් වැනි අනතුරුකාරී සත්වයෙක් සිටීදැයි පරික්ෂා කිරීම, බෑවුමක් සහිත ස්ථානක් නම් ලිස්සා වැටීමක් වැනි අවදානමක් වේදැයි විපරම් කිරීම ආදිය සැලකිය හැක.
..
R for Response (ප්රතිචාරය)
..
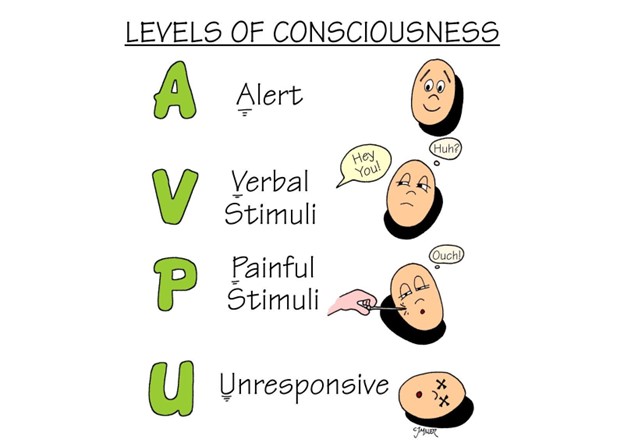
ඔබටත් රෝගියාටත් අනතුරක් නැතිනම් ඊලඟ අදියරට යා හැක. එනම් රෝගියාට සිහිය ඇතිදැයි සෙවීමයි. මේ සඳහා රෝගියාගෙන් යම් ප්රතිචාරයක් ලබා ගැනීමට අවශ්ය වන අතර එමඟින් ඔවුන්ගේ රෝගීතත්වයේ ස්වභාවය කුමක් දැයි අවබෝදයක්ද ලබාගත හැකිය. රෝගියාගේ ප්රතිචාර දැක්වීමේ හැකියාව නිර්ණය කිරීමට AVPU scale භාවිතා කල හැක.
..
..
..
..
..
ඊළඟ අදියරට පිවිසීමට පෙර රෝගියාගේ පිට කොන්දට ආබාධයක් සිදුවී ඇතිදැයි නිරීක්ෂණය කළ යුතුය. නැතිනම් රෝගියාගී තත්වය තවත් දරුණු විය හැක. බිම වැතිරී සිටින රෝගියාගේ පිට ප්රදේශයට දෑත් තබා තැල්මක් තිබේදැයි බලන්න. තැල්මක් තිබේනම් රෝගියාව සෙලවීමෑන් වළකින්න. එසේ නැතිනම් ඊළඟ අදියරට යා හැක. ඊට පෙර රෝගියාගේ සාක්කු වල තිබෙන දෑ, අත් ඔරලෝසු, මුදු ගලවා ඉවත් කරන්න.
..
A for Airway (ශ්වසන මාර්ගය)
..
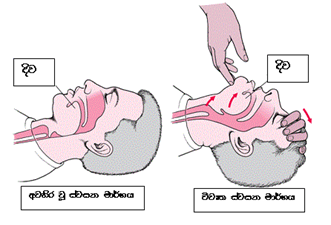
දැන් රෝගියා සිහිසුන් වී ඇත්තේ කුමක් නිසාද යන්න සෙවිය යුතුය. ඔබගේ එක් දනහිසක් රෝගියාගේ උරහිස ආසන්නයේද අනික ඔහුගේ වැලමිට ආසන්නයේද පවතින ලෙස දනගැසිය යුතුය. ඔබගේ එක් අතක් රෝගියාගේ නළලේද අනිත් අතේ ඇඟිලි දෙකක් නිකටේද තබා ඔහුගේ හිස ඔසවන්න. ඉන්පසු හක්ක දෙපසට ඇඟිලි දෙකක් තබා මුඛය විවෘත කර යම් බාධකයක් ඇතිදැයි බලන්න. එය ස්වසන මාර්ගයට හානි නොවන ලෙස ඉවත් කරන්න. එසේ කිරීමට නොහැකි නම් හදිසි අනතුරු සේවා පැමිණෙන තෙක් සිටින්න.
..
 ..
..
B for Breathing (ශ්වසන ක්රියාවලිය)
..
ශ්වසන මාර්ගයට බාධාවක් නැති විට රෝගියාගේ හුස්ම වාර ගණන් කරන්න (සාමාන්යය තත්පර 10කදී හුස්ම වාර දෙකක් පමණ ). පපුවේ චලනය (ඉහළ සහ පහළ) නිරීක්ෂණය සහ ඔබේ කන ඔවුන්ගේ මුඛයට සහ නාසයට ළං කර සවන් දීම මඟින් රෝගියා හුස්ම ගන්නේදැයි නිරීක්ෂණය කල හැක. ශ්වසන මාර්ගය පැහැදිලි නම් සහ ඔවුන් තවමත් හුස්ම නොගන්නේ නම්, රුධිර සංසරණය පරික්ෂා කල යුතුය. හුස්ම ගැනීම සාමාන්ය ලෙස සිදුවන්නේ නම් රෝගියාව ආරක්ෂිත ඉරියව්වේ තැබිය හැක.
..
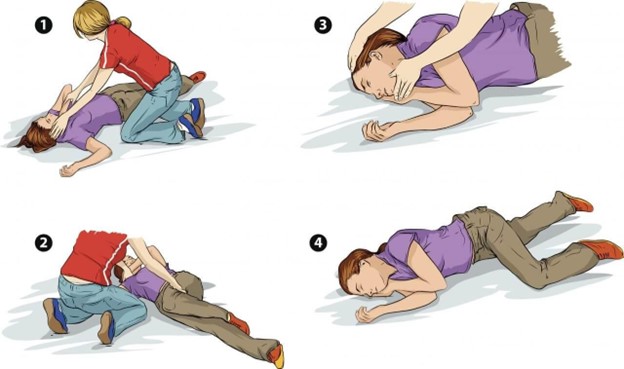
මෙහි ආරක්ෂිත ඉරියව්වට රෝගියා පෙරලීමේ පියවර පහත පෙන්වාදෙයි.
..
 ..
..
ආරක්ෂිත ඉරියව්වට පෙරලීමට හේතු කිහිපයක් නම්,
..
C for Circulation (රුධිර සංසරණය)
..
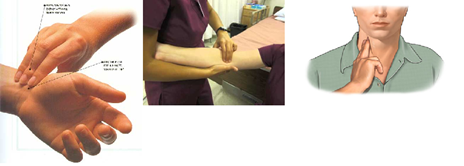
රෝගියා හුස්ම ගන්නේ නැති නම්, ඔහුගේ රුධිර සංසරණය පරීක්ෂා කළ යුතු වේ. මෙය, ඔබගේ මැදැඟිල්ල සහ වෙදැඟිල්ල හෝ දබරැඟිල්ල සහ මැදැඟිල්ල රෝගියාගේ කැරෝටීය ධමනිය මත (බෙල්ලේ) හෝ අරීය ධමනිය (මැනික්කටුවේ ) මත තබා පරික්ෂා කළ හැක. (සාමාන්ය අගය විනාඩියට වාර 40ක් පමණ වේ) මේ අවස්ථාවේ රෝගියාගේ ජීවිතයට අනතුරක් ඇති නිසා CPR ලබාදිය යුතු වේ.
..
ඔබ පුහුණු ප්රථමාධාරකරුවෙකු නොවන්නේ නම් CPR (කන්ථුක පුප්පුශීය ප්රතිප්රබෝධනය) කිරීමෙන් වැලකී සිටිය යුතුය. ඔබගේ වරදින් ඉළ ඇට භග්නයක් සිදුවීමට ඉඩ ඇති අතර මෙමඟින් රෝගියා ජීවිතක්ශයට පත්වී ඔහුගේ මරනයට ඔබට වගකීමට සිදුවනු ඇත. පහත රූපයේ පෙන්වා ඇති ස්ථාන වලින් පහසුවෙන්ම නාඩි පරික්ෂා කල හැක.
..
 ..
..
Imagine yourself walking through a trail, enjoying the view, when all of a sudden you see a person laying on the ground in front of you. What would you do, and how would you manage this situation? Fear not, because DR. ABC is here to help. The DRABC procedure or the primary survey will allow you to determine what level of first aid you need to administer and decide whether you need to call the emergency services. First aiders split the primary survey into the steps D-R-A-B-C, you can remember this easily by remembering it as DR. ABC. Let’s get to know the doctor even better.
..
D for Danger
..
As the first step, you need to assess the environment around the person laying on the ground to see if there is any immediate danger to you or them. If it is not safe for you to reach the patient, DO NOT, because you have to save yourself before anyone else. Otherwise there will be another patient. However, if it is safe for you but not for the patient, you may carry or drag them to safety. If not, you can apply the rest of DRABC on the spot. As some examples, be mindful about the presence of reptiles like snakes around the patient or the possibility of slipping down if it's a slope.
..
R for Response
..
Once you and the patient are clear of any danger, you may check if the patient is conscious or not by following these simple steps. For this, you need to receive some response from the patient and through that you can get an idea about the nature of the unease within the patient. The AVPU Scale can be applied for that purpose.
..
..
..
..
..
Before moving to the next step, you must verify that the patient does not have a spinal fracture, otherwise you might worsen their condition. If the person is on their back, gently place your arms under their back and slide them down to check for swelling. If you can confirm their spine is fractured, do not move the patient. If there is no sign of that, check their pockets for any sharp items that may cause harm and remove them. This includes wrist watches and rings on their arms as well.
..
A for Airway
..
Now you must check why the patient is unresponsive. Get on to your knees next to the patient, in a way such that one knee is in front of the patient's shoulder, while the other is in front of their elbow. Place your hand on their forehead and two fingers of the other hand on their chin and tilt the head up. Then place two fingers on the opposite ends of the patient’s jaw and open their mouth to check if there is anything blocking the airway. If there is something, and looks like it will not damage the airway, take it out. If it is stuck, wait for professional help.
..
B for Breathing
..
When the airway is open; look out for any signs of normal breathing (around 2 breaths in 10 seconds). By observing the movement of the chest (Up and down) and listening by placing your ear near their mouth or nose, you can confirm whether the patient is breathing. If they are not breathing even if the airway is clear, the blood circulation must be checked. Look out for if the patient looks to be breathing abnormally, infrequently or not at all.
..
If the casualty is unresponsive but is breathing normally and isn’t in a state where they can be moved without damaging them further put them into the recovery position.
..
Here is a step by step guide on how to place the patient in recovery position:
..
The purpose of the recovery position is that it;
..
C for Circulation
..
If the patient is not breathing, you may check their blood circulation through placing your ring finger and middle finger (Index finger and middle finger are also used) on their carotid artery in the neck or radial artery in their wrist. If the pulse is abnormal (normal is 40 beats per minute) call a professional and emergency service (TP No: 110) to apply CPR (Cardiopulmonary resuscitation).
..
It is not advised to perform CPR if you are not a professional as too much force may result in rib cage fractures and you will be liable for the death of the patient.
2423